Logical Model Reference¶
Model - Cubes meta-data objects and functionality for working with them. Logical Model and Metadata
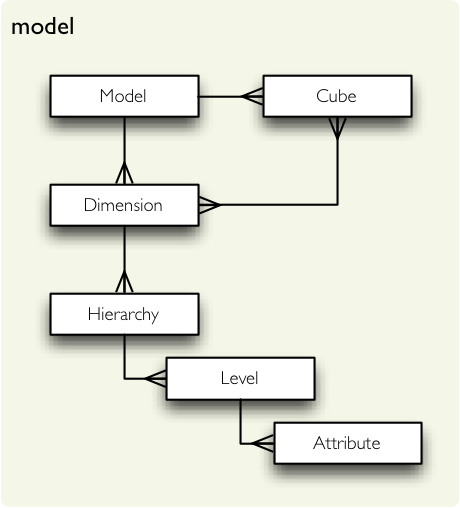
The logical model classes.
Loading or creating a model¶
- cubes.load_model(resource, translations=None)¶
Load a model from resource which can be a filename, URL, file-like object or a directory path.
If a resource is a directory it is considered a model bundle and has to have the following contents:
- model.json – main model file
- dim_*.json - files with dimension defition, one dimension per file
- cube_*.json - files with cube definition, one cube per file
- cubes.create_model(model, cubes=None, dimensions=None, translations=None)¶
Create a model from a model description dictionary in model. This is designated way of creating the model from a dictionary.
cubes or dimensions are list of their respective dictionary definitions. If definition of a cube in cubes or dimension in dimensions already exists in the model, then ModelError is raised.
The model dictionary contains main model description. The structure is:
{ "name": "public_procurements", "label": "Procurements", "description": "Procurement Contracts of an Organisation" "cubes": [...] "dimensions": [...] }translations is a dictionary where keys are locale names and values are translation dictionaries. See Model.localize() for more information.
- cubes.create_cube(desc, dimensions, model_mappings=None)¶
Creates a Cube instance from dictionary description desc with dimension dictionary in dimensions
In file based model representation, the cube descriptions are stored in json files with prefix cube_ like cube_contracts, or as a dictionary for key cubes in the model description dictionary.
JSON example:
{ "name": "contracts", "measures": ["amount"], "dimensions": [ "date", "contractor", "type"] "details": ["contract_name"], }
- cubes.create_dimension(obj, dimensions=None)¶
Creates a Dimension instance from obj which can be a Dimension instance or a string or a dictionary. If it is a string, then it represents dimension name, the only level name and the only attribute.
Keys of a dictionary representation:
name: dimension name
levels: list of dimension levels (see: cubes.Level)
- hierarchies or hierarchy: list of dimension hierarchies or
list of level names of a single hierarchy. Only one of the two should be specified, otherwise an exception is raised.
default_hierarchy_name: name of a hierarchy that will be used when no hierarchy is explicitly specified
label: dimension name that will be displayed (human readable)
description: human readable dimension description
info - custom information dictionary, might be used to store application/front-end specific information (icon, color, ...)
template – name of a dimension to be used as template. The dimension is taken from dimensions argument which should be a dictionary of already created dimensions.
Defaults
- If no levels are specified during initialization, then dimension name is considered flat, with single attribute.
- If no hierarchy is specified and levels are specified, then default hierarchy will be created from order of levels
- If no levels are specified, then one level is created, with name default and dimension will be considered flat
String representation of a dimension str(dimension) is equal to dimension name.
Class is not meant to be mutable.
Raises ModelInconsistencyError when both hierarchy and hierarchies is specified.
- cubes.create_level(obj)¶
Creates a level from obj which can be a Level instance, string or a dictionary. If it is a string, then the string represents level name and the only one attribute of the level. If obj is a dictionary, then the keys are:
- name – level name
- attributes – list of level attributes
- key – name of key attribute
- label_attribute – name of label attribute
Defaults:
- if no attributes are specified, then one is created with the same name as the level name.
Simple Models¶
There might be cases where one would like to analyse simple (denormalised) table. It can be either a table in a database or data from a single CSV file. For convenience, there is an utility function called simple_model that will create a model with just one cube, simple dimensions and couple of specified measures.
- cubes.simple_model(cube_name, dimensions, measures)¶
Create a simple model with only one cube with name cube_name`and flat dimensions. `dimensions is a list of dimension names as strings and measures is a list of measure names, also as strings. This is convenience method mostly for quick model creation for denormalized views or tables with data from a single CSV file.
Example:
model = simple_model("contracts", dimensions=["year", "supplier", "subject"], measures=["amount"]) cube = model.cube("contracts") browser = workspace.create_browser(cube)
Model components¶
Model¶
- class cubes.Model(name=None, cubes=None, dimensions=None, locale=None, label=None, description=None, info=None, mappings=None, **kwargs)¶
Logical Model represents analysts point of view on data.
Attributes:
- name - model name
- cubes - list of Cube instances
- dimensions - list of Dimension instances
- locale - locale code of the model
- label - human readable name - can be used in an application
- description - longer human-readable description of the model
- info - custom information dictionary
- mappings – model-wide mappings of logical-to-physical attributes
The mappings is a dictiononary of form:
{ "cubes": { "cube_name" : { ... } }, "dimensions": { "dimension_name" : { "dimension_attribute": "physical_attribute" } } }
The mappings in cubes are the same as mappings in the Cube definition. The logical name (keys) of dimension mappings is just dimension attribute name without the dimension prefix.
- add_cube(cube)¶
Adds cube to the model and also assigns the model to the cube. If cube has a model assigned and it is not this model, then error is raised.
Raises ModelInconsistencyError when trying to assing a cube that is already assigned to a different model or if trying to add a dimension with existing name but different specification.
- add_dimension(dimension)¶
Add dimension to model. Replace dimension with same name
- cube(cube)¶
Get a cube with name name or coalesce object to a cube.
- dimension(dim)¶
Get dimension by name or by object. Raises NoSuchDimensionError when there is no dimension dim.
- is_valid(strict=False)¶
Check whether model is valid. Model is considered valid if there are no validation errors. If you want to be sure that there are no warnings as well, set strict to True. If strict is False only errors are considered fatal, if True also warnings will make model invalid.
Returns True when model is valid, otherwise returns False.
- localizable_dictionary()¶
Get model locale dictionary - localizable parts of the model
- localize(translation)¶
Return localized version of the model.
translation might be a string or a dicitonary. If it is a string, then it represents locale name from model’s localizations provided on model creation. If it is a dictionary, it should contains full model translation that is going to be applied.
Translation dictionary structure example:
{ "locale": "sk", "cubes": { "sales": { "label": "Predaje", "measures": { "amount": "suma", "discount": {"label": "zľava", "description": "uplatnená zľava"} } } }, "dimensions": { "date": { "label": "Dátum" "attributes": { "year": "rok", "month": {"label": "mesiac"} }, "levels": { "month": {"label": "mesiac"} } } } }Note
Whenever master model changes, you should call this method to get actualized localization of the original model.
- remove_cube(cube)¶
Removes cube from the model
- remove_dimension(dimension)¶
Remove a dimension from receiver
- to_dict(**options)¶
Return dictionary representation of the model. All object references within the dictionary are name based
- expand_dimensions - if set to True then fully expand dimension information in cubes
- full_attribute_names - if set to True then attribute names will be written as dimension_name.attribute_name
- validate()¶
Validate the model, check for model consistency. Validation result is array of tuples in form: (validation_result, message) where validation_result can be ‘warning’ or ‘error’.
Returs: array of tuples
Cube¶
- class cubes.Cube(name, dimensions=None, measures=None, model=None, label=None, details=None, mappings=None, joins=None, fact=None, key=None, description=None, options=None, info=None, **kwargs)¶
Create a new Cube model.
Attributes:
- name: cube name
- measures: list of measure attributes
- dimensions: list of dimensions (should be Dimension instances)
- model: model the cube belongs to
- label: human readable cube label
- details: list of detail attributes
- description - human readable description of the cube
- key: fact key field (if not specified, then backend default key will be used, mostly id for SLQ or _id for document based databases)
- info - custom information dictionary, might be used to store application/front-end specific information
Attributes used by backends:
- mappings - backend-specific logical to physical mapping dictionary
- joins - backend-specific join specification (used in SQL backend)
- fact - fact dataset (table) name (physical reference)
- options - dictionary of other options used by the backend - refer to the backend documentation to see what options are used (for example SQL browser might look here for denormalized_view in case of denormalized browsing)
- add_dimension(dimension)¶
Add dimension to cube. Replace dimension with same name. Raises ModelInconsistencyError when dimension with same name already exists in the receiver.
- dimension(obj)¶
Get dimension object. If obj is a string, then dimension with given name is returned, otherwise dimension object is returned if it belongs to the cube.
Raises NoSuchDimensionError when there is no such dimension.
- measure(obj)¶
Get measure object. If obj is a string, then measure with given name is returned, otherwise measure object is returned if it belongs to the cube. Returned object is of Attribute type.
Raises NoSuchAttributeError when there is no such measure or when there are multiple measures with the same name (which also means that the model is not valid).
- remove_dimension(dimension)¶
Remove a dimension from receiver. dimension can be either dimension name or dimension object.
- to_dict(expand_dimensions=False, with_mappings=True, **options)¶
Convert to a dictionary. If expand_dimensions is True (default is False) then fully expand dimension information If with_mappings is True (which is default) then joins, mappings, fact and options are included. Should be set to False when returning a dictionary that will be provided in an user interface or through server API.
- validate()¶
Validate cube. See Model.validate() for more information.
Dimension, Hierarchy, Level¶
- class cubes.Dimension(name, levels, hierarchies=None, default_hierarchy_name=None, label=None, description=None, info=None, **desc)¶
Create a new dimension
Attributes:
- name: dimension name
- levels: list of dimension levels (see: cubes.Level)
- hierarchies: list of dimension hierarchies. If no hierarchies are specified, then default one is created from ordered list of levels.
- default_hierarchy_name: name of a hierarchy that will be used when no hierarchy is explicitly specified
- label: dimension name that will be displayed (human readable)
- description: human readable dimension description
- info - custom information dictionary, might be used to store application/front-end specific information (icon, color, ...)
Dimension class is not meant to be mutable. All level attributes will have new dimension assigned.
Note that the dimension will claim ownership of levels and their attributes. You should make sure that you pass a copy of levels if you are cloning another dimension.
- all_attributes()¶
Return all dimension attributes regardless of hierarchy. Order is not guaranteed, use cubes.Hierarchy.all_attributes() to get known order. Order of attributes within level is preserved.
- attribute(reference)¶
Get dimension attribute from reference.
- default_hierarchy¶
Get default hierarchy specified by default_hierarchy_name, if the variable is not set then get a hierarchy with name default
Warning
Depreciated. Use Dimension.hierarchy() instead.
- has_details¶
Returns True when each level has only one attribute, usually key.
- hierarchy(obj=None)¶
Get hierarchy object either by name or as Hierarchy. If obj is None then default hierarchy is returned.
- is_flat¶
Is true if dimension has only one level
- key_attributes()¶
Return all dimension key attributes, regardless of hierarchy. Order is not guaranteed, use a hierarchy to have known order.
- level(obj)¶
Get level by name or as Level object. This method is used for coalescing value
- level_names¶
Get list of level names. Order is not guaranteed, use a hierarchy to have known order.
- levels¶
Get list of all dimension levels. Order is not guaranteed, use a hierarchy to have known order.
- to_dict(**options)¶
Return dictionary representation of the dimension
- validate()¶
Validate dimension. See Model.validate() for more information.
- class cubes.Hierarchy(name, levels, dimension=None, label=None, info=None)¶
Dimension hierarchy - specifies order of dimension levels.
Attributes:
- name: hierarchy name
- dimension: dimension the hierarchy belongs to
- label: human readable name
- levels: ordered list of levels or level names from dimension
- info - custom information dictionary, might be used to store application/front-end specific information
Some collection operations might be used, such as level in hierarchy or hierarchy[index]. String value str(hierarchy) gives the hierarchy name.
- all_attributes()¶
Return all dimension attributes as a single list.
- is_last(level)¶
Returns True if level is last level of the hierarchy.
- key_attributes()¶
Return all dimension key attributes as a single list.
- level_index(level)¶
Get order index of level. Can be used for ordering and comparing levels within hierarchy.
- levels_for_depth(depth, drilldown=False)¶
Returns levels for given depth. If path is longer than hierarchy levels, cubes.ArgumentError exception is raised
- levels_for_path(path, drilldown=False)¶
Returns levels for given path. If path is longer than hierarchy levels, cubes.ArgumentError exception is raised
- next_level(level)¶
Returns next level in hierarchy after level. If level is last level, returns None. If level is None, then the first level is returned.
- path_is_base(path)¶
Returns True if path is base path for the hierarchy. Base path is a path where there are no more levels to be added - no drill down possible.
- previous_level(level)¶
Returns previous level in hierarchy after level. If level is first level or None, returns None
- rollup(path, level=None)¶
Rolls-up the path to the level. If level is None then path is rolled-up only one level.
If level is deeper than last level of path the cubes.HierarchyError exception is raised. If level is the same as path level, nothing happens.
- to_dict(**options)¶
Convert to dictionary. Keys:
- name: hierarchy name
- label: human readable label (localizable)
- levels: level names
- class cubes.Level(name, attributes, dimension=None, key=None, order_attribute=None, order=None, label_attribute=None, label=None, info=None)¶
Object representing a hierarchy level. Holds all level attributes.
This object is immutable, except localization. You have to set up all attributes in the initialisation process.
Attributes:
- name: level name
- dimension: dimnesion the level is associated with
- attributes: list of all level attributes. Raises ModelError when attribute list is empty.
- key: name of level key attribute (for example: customer_number for customer level, region_code for region level, month for month level). key will be used as a grouping field for aggregations. Key should be unique within level. If not specified, then the first attribute is used as key.
- order: ordering of the level. asc for ascending, desc for descending or might be unspecified.
- order_attribute: name of attribute that is going to be used for sorting, default is first attribute (usually key)
- label_attribute: name of attribute containing label to be displayed (for example: customer_name for customer level, region_name for region level, month_name for month level)
- label: human readable label of the level
- info: custom information dictionary, might be used to store application/front-end specific information
- attribute(name)¶
Get attribute by name
- has_details¶
Is True when level has more than one attribute, for all levels with only one attribute it is False.
- to_dict(full_attribute_names=False, **options)¶
Convert to dictionary
- class cubes.Attribute(name, label=None, locales=None, order=None, description=None, dimension=None, aggregations=None, info=None, format=None, **kwargs)¶
Cube attribute - represents any fact field/column
Attributes:
- name - attribute name, used as identifier
- label - attribute label displayed to a user
- locales = list of locales that the attribute is localized to
- order - default order of this attribute. If not specified, then order is unexpected. Possible values are: 'asc' or 'desc'. It is recommended and safe to use Attribute.ASC and Attribute.DESC
- aggregations - list of default aggregations to be performed on this attribute if it is a measure. It is backend-specific, but most common might be: 'sum', 'min', 'max', ...
- info - custom information dictionary, might be used to store application/front-end specific information
- format - application-specific display format information, useful for formatting numeric values of measure attributes
String representation of the Attribute returns its name (without dimension prefix).
cubes.ArgumentError is raised when unknown ordering type is specified.
- full_name(dimension=None, locale=None, simplify=True)¶
Return full name of an attribute as if it was part of dimension. Append locale if it is one of of attribute’s locales, otherwise raise cubes.ArgumentError.
- ref(simplify=True, locale=None)¶
Return full attribute reference. Append locale if it is one of of attribute’s locales, otherwise raise cubes.ArgumentError. If simplify is True, then reference to an attribute of flat dimension without details will be just the dimension name.
Warning
This method might be renamed.
Helper function to coalesce list of attributes, which can be provided as strings or as Attribute objects:
- cubes.attribute_list(attributes, dimension=None, attribute_class=None)¶
Create a list of attributes from a list of strings or dictionaries. see cubes.coalesce_attribute() for more information.
- exception ModelError¶
Exception raised when there is an error with model and its structure, mostly during model construction.
- exception ModelIncosistencyError¶
Raised when there is incosistency in model structure, mostly when model was created programatically in a wrong way by mismatching classes or misonfiguration.
- exception NoSuchDimensionError¶
Raised when a dimension is requested that does not exist in the model.
- exception NoSuchAttributeError¶
Raised when an unknown attribute, measure or detail requested.