Data Pipes and Data Processing Streams¶
Data processing stream is a network of data processing nodes connected by data pipes. There are several data processing node types:
- source nodes - provide data from data sources such as CSV files or database tables
- target nodes - nodes for consuming data and storing them or creating data visualisations
- record nodes - perform operations on whole records, such as merging, joining, aggregations
- field nodes - perform operations on particuliar fields, such as text substitution, field renaming, deriving new fields, restructuring
See also
Stream class documentation: brewery.pipes.Stream
Data Processing Streams¶
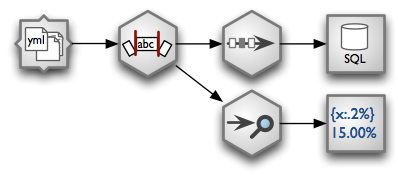
Example of a processing stream:
- load YAML fiels from a directory - each file represents one record
- Strip all string fields.
- Remove duplicates and store unique records in a SQL database table
- Perform data audit and pretty-print it using formatted text printer
# Prepare nodes
nodes = {
"source": pipes.YamlDirectorySourceNode(path = "data/donations"),
"strip": pipes.StringStripNode(),
"distinct": pipes.DistinctNode(keys = ["year", "receiver", "project"]),
"target": pipes.SQLTableTarget(url = "postgres://localhost/data", table = "donations"),
"audit": pipes.AuditNode(),
"print": pipes.FormattedPrinterNode(output = "audit.txt")
}
# Configure nodes
nodes["source"].fields = ds.fieldlist([ ("year", "integer"),
("receiver", "string"),
("project", "string"),
("requested_amount", "float"),
("received_amount", "float"),
("source_comment", "string")])
nodes["print"].header = u"field nulls empty\n" \
"-----------------------------------------------"
nodes["print"].format = u"{field_name:<30.30} {null_record_ratio:3.2%} {empty_string_count:>10}"
connections = [ ("source", "strip"),
("strip", "distinct"),
("distinct", "target"),
("strip", "audit"),
("audit", "print")
]
# Create and run stream
stream = pipes.Stream(nodes, connections)
stream.initialize()
stream.run()
stream.finalize()
The created audit.txt file will contain:
field nulls empty
-----------------------------------------------
year 0.00% 0
receiver 0.00% 5
project 0.51% 0
requested_amount 0.70% 0
received_amount 6.40% 0
source_comment 99.97% 0
See also
For more information about nodes see Node Reference
Running Streams¶
Streams are being run using Stream.run(). Stream has to be initialized before running. Stream is run in parallel - each node is run in separate thread.